The following experiments with Agnihotra and Homa Therapy were conducted at Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Ooty, Tamil Nadu, India under the direction of Prof N. Selvaraj.
Preamble
Homa Organic Farming has a strong potential for increasing the yield and quality in plant production. It also seems to be capable of regulating insect infestation and fungal disease in crops in an ecologically sound manner. In addition, soil characteristics with significant effect on yield such as plant availability of nutrients appear to be improved by this technique. Thus it will be particularly interesting for organic farmers, as it may apply as a complementary method together with common methods of organic farming.
Experimental Details
To increase the yield and to improve the quality of Rose, Gerbera, Carnation, Potato, Cabbage under the organic farming system with Agnihotra, trials were laid out in the farms of Institute of Commercial Horticulture, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Ooty. The experiments consisted of the following four treatments:
- T1 Organic farming system
- T2 Organic farming system + Agnihotra
- T3 Conventional
- T4 Absolute control
Rose
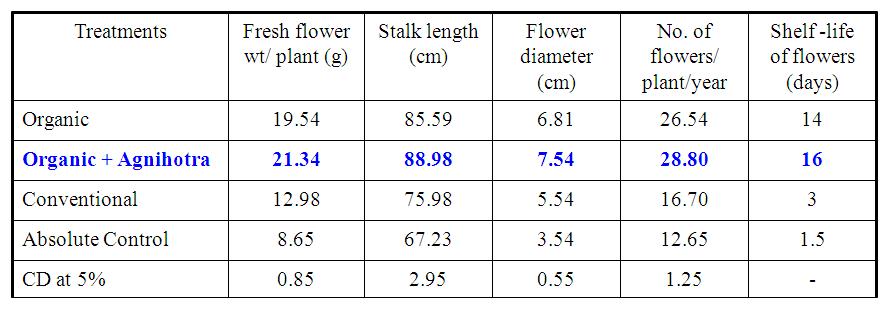
Table 1. Effect of Homa organic farming on growth and yield of Rose cv. Passion
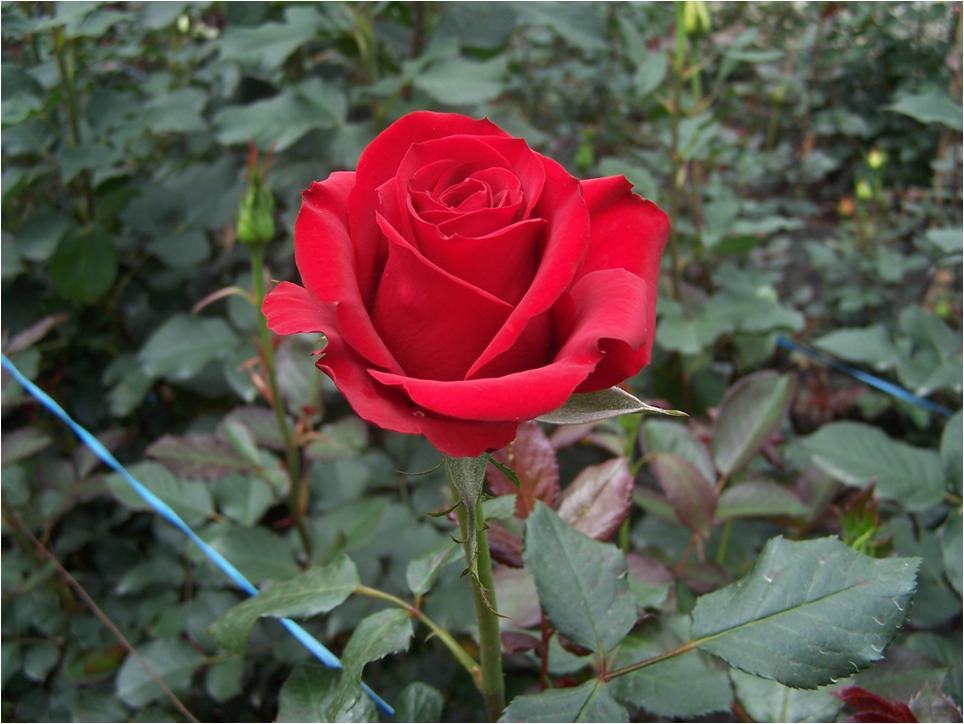


(Photos l to r: powdery mildew on Rose; healthy Homa Rose cv. Passion)
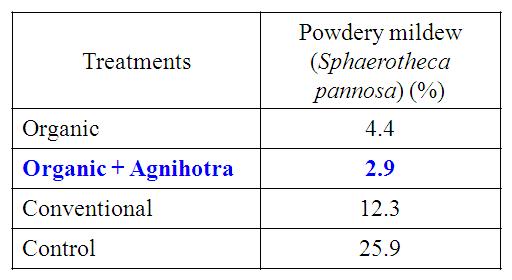
Table 2. Effect of Homa organic farming on the incidence of Powdery mildew of Rose cv. Passion
Salient Findings
- Among the four treatments Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) in Rose recorded higher performance for fresh flower wt/ plant 21.34 (g), Stalk length 88.98(cm), Flower diameter 7.54 (cm), No. of flowers/plant/year 28.80, and higher shelf life of flowers 16 (days) (Table 1).
- Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) showed higher disease resistance in Rose (Table 2).
Carnation
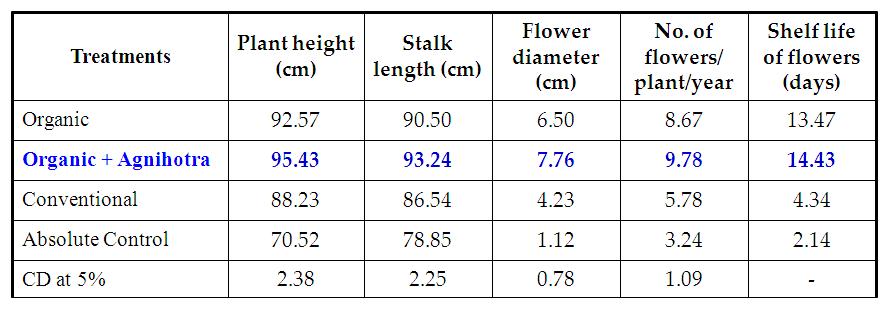
Table 3. Effect of Agnihotra on growth and yield of Carnation var. Chipro


(Photos l to r: fusarium root rot on Carnation; healthy Homa carnations
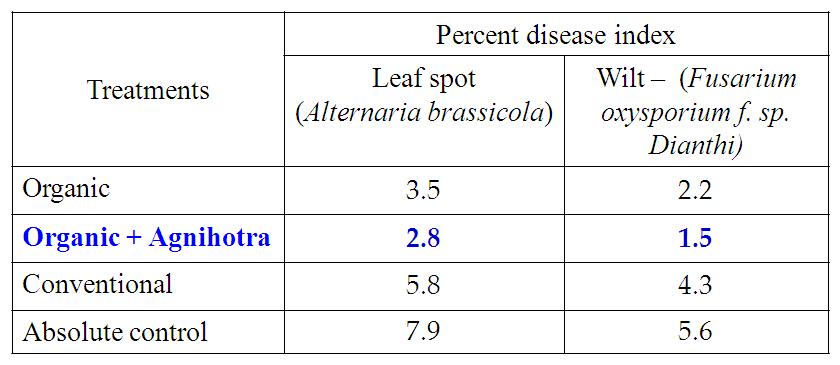
Table 4. Effect of Agnihotra on the incidence of Fusarium wilt of Carnation var. Chipro
Salient Findings
- Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) in Carnation recorded higher performance for Plant height 95.43 (cm), stalk length 93.24(cm), Flower diameter 7.76(cm), Number of flowers/plant/year 9.78, Shelf life 14.43(days) compared to other treatments (Table 3).
- In Carnation, Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) showed higher disease resistance (Table 4).
Gerbera
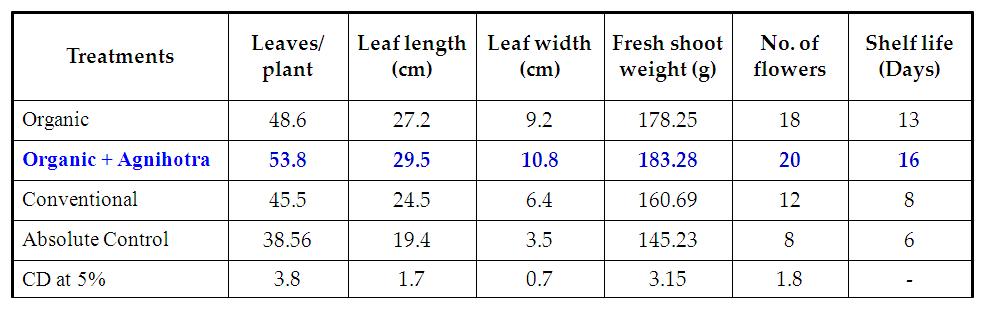
Table 5. Effect of Agnihotra on the growth and yield of Gerbera cv. Ruby Red
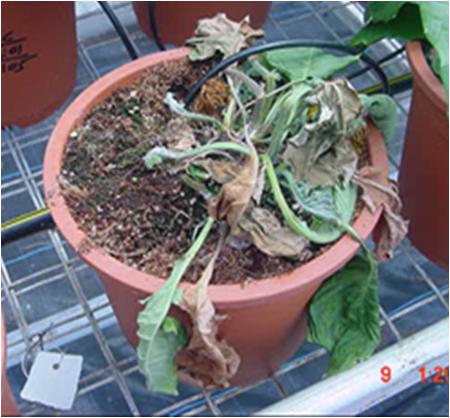


(Photos l to r: fusarium wilt on Gerbera; healthy Homa gerberas
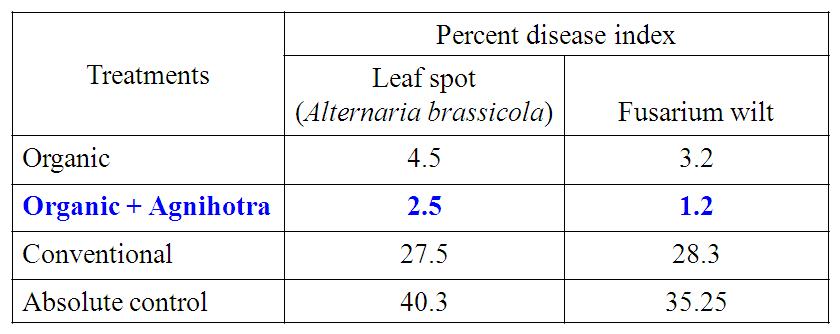
Table 6. Effect of Agnihotra on the incidence of leaf spot and root rot of Gerbera cv. Ruby Red
Salient Findings
- In Gerbera, Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) recorded higher performance for number of flowers 20, Shelf life 16 days (Table 5).
- In Gerbera, Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) showed higher disease resistance for leaf spot, fusarium wilt. (Table 6).
Cabbage
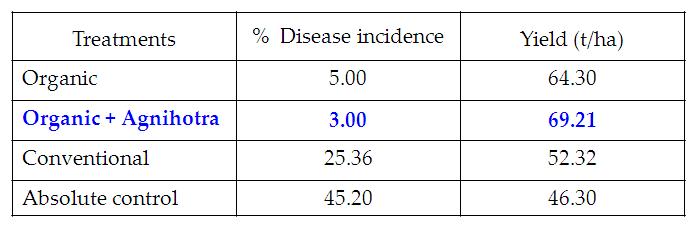
Table 7. Effect of Agnihotra on yield and the incidence of leaf spot disease in Cabbage variety Questo
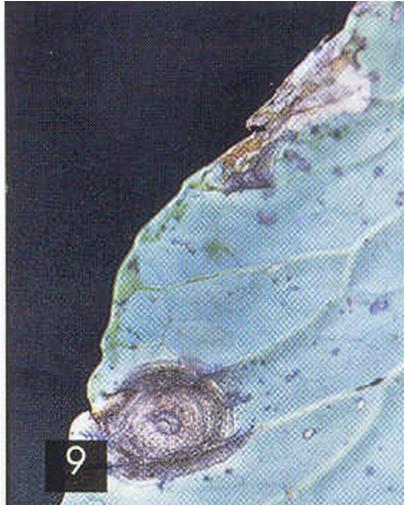


(Photos l to r: alternaria leaf spot; downy mildew; healthy Homa cabbage)
Salient Findings
- In Cabbage, Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) recorded higher performance for yield 69.21 t/ha and showed increased disease resistance. (Table 8).
Potato
Table 8. Effect of Agnihotra on pest complex of Potato cv. Kufri jyoti
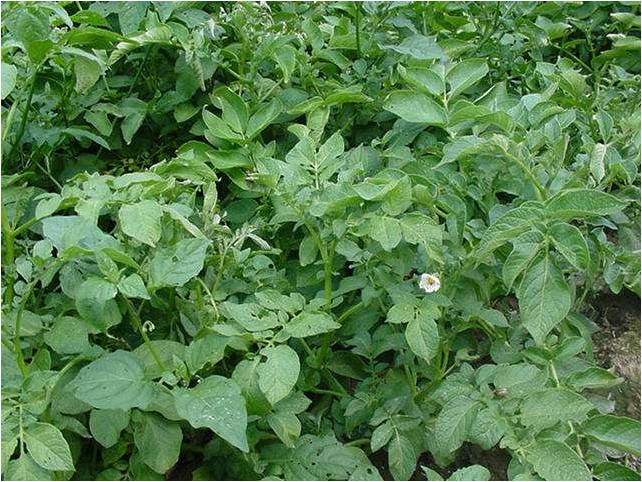
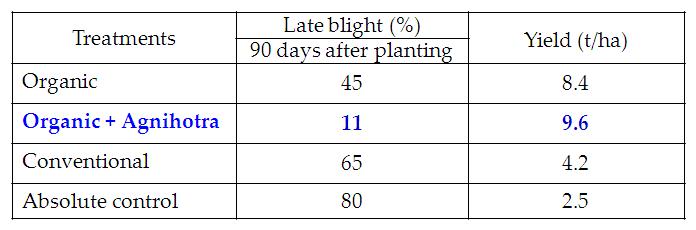


(Photos l to r: late blight in potato; healthy Homa potato)
Salient Findings
- Among the four treatments Organic farming with Agnihotra (T2) in Potato recorded higher performance for yield 9.6 t/ha and showed increased disease resistance. (Table 7).
CONCLUSION:
In every study, organic farming with Agnihotra had the highest performance in every category. The results conclusively show that Agnihotra is a highly effective method for producing healthy, organic food without the need of pesticides, fertilizers or herbicides.

